Chemical Management
Governance and Management Framework
Under the Responsible Care advancement structure, in Japan, the dedicated chemical product management team deals with matters relating to legal compliance, SDS, and customer outreach for exported goods. Overseas, we have established a structure to promote chemical management with local subsidiaries playing a central role. Under this structure, we quickly identify and respond in a planned manner to changes in the environment and trends in the relevant laws/regulations in Japan and overseas.
In 2019, we launched an overseas legal management organization to broadly collect legal information from overseas, such as from industry organizations, and promptly share information with all of JSR, including Group companies and local subsidiaries, to support the rapid tightening of regulations abroad and new legislations in various countries.
Going forward, we will continue to flexibly review our structures based on our Group’s business and trends in Japan and overseas.
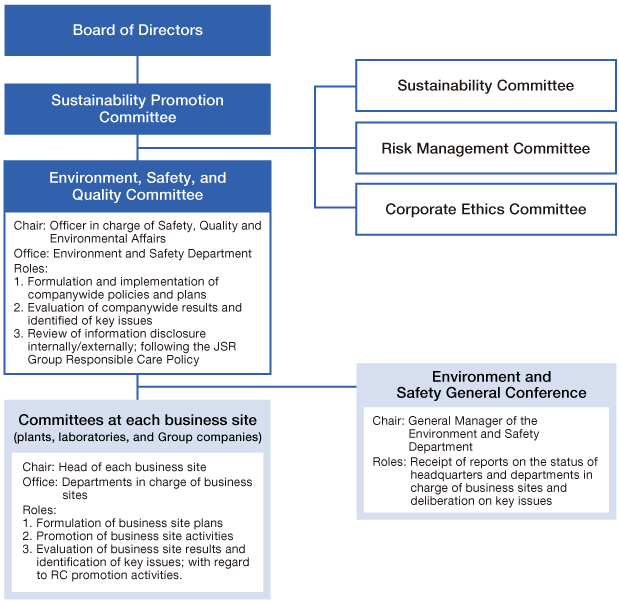
Please refer to the two pages below for the details of our structures.
Policy and Basic Approach
In light of recent global trends in chemical management, JSR group has established the following three policies in its environment and safety management organization by which chemical management is implemented.
- 1.Instead of hazard-based management*1, we will endeavor to implement risk-based management*2.
- 2.We will strive to manage our entire supply chain by utilizing a globally standardized method.
- 3.To ensure product safety, we will advance self-motivated initiatives to systematically reduce hazardous chemicals in addition to complying with regulations.
- *1Hazard-based management: Management based solely on the hazardous properties of substances
- *2Risk-based management: Management based on exposure to the hazardous properties of substances
Initiatives
1. Voluntary Approaches to Systematically Reduce Toxic Chemicals
JSR group systematically implements approaches to reduce and eliminate toxic chemicals starting in the product design stage. The chemicals subject to management are those listed in laws and regulations of various countries and customers’ management standards as well as general chemicals not included in those lists. For all of these chemicals, specialists implement reviews during each step – from raw materials procurement to design, development, trial manufacture, customer evaluation, and commercialization. In this way, we are striving to minimize the risks that JSR products have on people’s health and the environment.
(1) Response to Regulations of Various Countries and Customer Management Standards
Substances of which the manufacture and use are prohibited or restricted in the laws of major countries are investigated in detail starting with the raw materials selection stage, and their use, byproducts and mixing in products is strictly managed. The lists of substances covered are as shown below. Among these, ① to ⑥ are those for which use in JSR group materials/products is prohibited. Those in ⑦to ⑯ are those for which risks are evaluated by intended use when reviews are conducted in the development stage, and for which the possibility of use and necessity of review of alternative substances are confirmed.
In recent years, regulatory laws on chemicals have been legislated/amended in various countries across the world. As such, JSR confirms the regulated substances in applicable countries and checks their usage restrictions in a framework for reviewing commercialization in response to the expansion of countries to which our products are exported.
List of major chemical substance regulations subject to survey
①(Japan) Act on the Regulation of Manufacture and Evaluation of Chemical Substances Class I Specified Chemical Substances
②(Japan) Article 55 of Industrial Safety and Health Act and Article 16 of Enforcement Order of the Industrial Safety and Health Act (Harmful Substances, etc., Prohibited for Manufacturing, etc.)
③(Japan) Article 2 of Act on Special Measures against Dioxins
④(Japan) “Specified Poisonous Substances” as specified in the Poisonous and Deleterious Substances Control Act and Cabinet Order for the Designation of the Poisonous and Deleterious Substances
⑤(UN) Annexes A, B, and C of Stockholm Convention on POPs
⑥(US) Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA) Prohibited or Restricted Substances in Section 6
⑦(Japan) Act on the Regulation of Manufacture and Evaluation of Chemical Substances Class II Specified Chemical Substances and Monitoring Chemical Substances
⑧(EU) ELV Directive
⑨(EU) RoHS Directive Annex II
⑩(EU) POPs Regulation Annex I
⑪(EU) REACH Regulation Candidate List of SVHC for Authorization and Annex XIV (Authorization List)
⑫(EU) REACH Regulation Annex XVII (Restricted Substances)
⑬(EU) Medical Devices Regulation (MDR) Annex I 10.4 Chemical Substances
⑭(China) Administrative Measures for the Restriction of the Use of Hazardous Substances in Electrical and Electronic Products
⑮Global Automotive Declarable Substance List (GADSL)
⑯IEC 62474 DB Declarable substance groups and declarable substances
2. Approaches to Reducing and Eliminating Toxic Substances and Substances of Concern Across All Chemicals
Even for chemical substances not regulated by law, JSR group implements verifications of toxicity during reviews in the raw materials selection stage, design and prototype stage, regardless of whether it is an existing chemical substance or new chemical substance. In cases where it is judged as being necessary, JSR also takes measures such as limiting use. In recent years in particular, JSR has been implementing investigations and analyses of substance information, safety information and country registration information for impurities found in existing chemical substances in the raw materials selection stage. This is part of an effort to strengthen checks to make sure that raw materials containing toxic substances and substances of concern are not used erroneously.
For substances where there are concerns regarding continuity of future use due to the chemical structure of the substance or trends in risk evaluations of each country, our Chemical Products Management Dept. regularly gathers information and makes the business departments and R&D Dept. aware that such substances are toxic substances and substances of concern for which substitution and elimination should be examined starting in the design stage. We examine their elimination in reviews leading up to commercialization. (See diagram below*3)
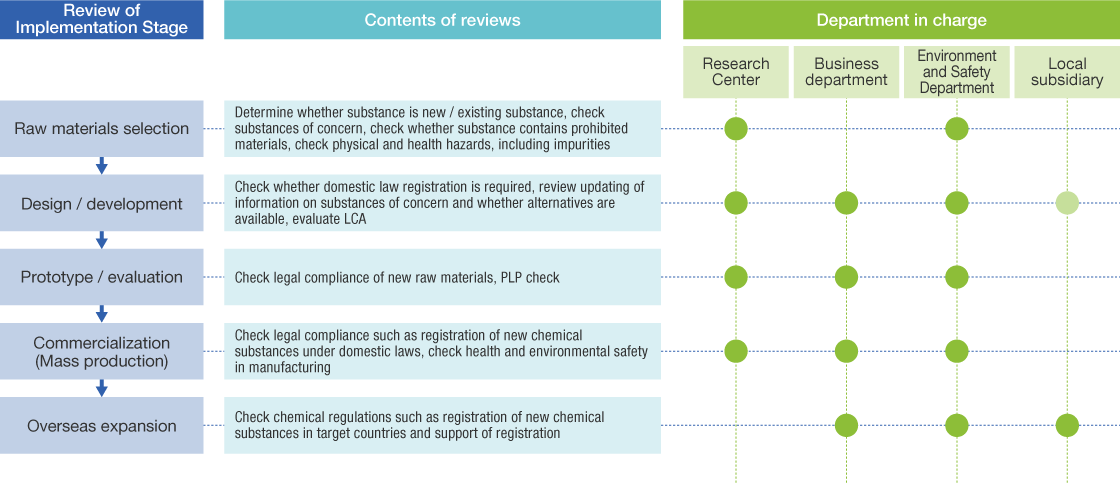
*3 This diagram features only contents of support related to chemical products. In each review, however, quality, specifications, manufacturing techniques, etc. are also checked simultaneously.
3. Compliance with Laws / Regulations and Standards
(1) Response to Chemical Product-related Domestic Laws and Regulations
In 2017, the Law concerning Pollutant Release and Transfer Register in Japan*4 was amended, and the revised portion of this Act which is concerned with the confirmation system used for low volume new chemical substances came into effect in 2019. JSR group has been responding without problem since the revision to the act. This includes dealing with requirements such as for usage certificates for each substance as newly needed due to this revision.
In addition, in preparation for the expansion of substances subject to risk management following the enforcement of the revised Industrial Safety and Health Act in 2024, we have been taking measures such as system modifications for the revisions to SDS*5. For substances subject to addition in 2024 and 2025, we began including them in SDS at the same time as their respective enforcement dates. We will also continue to systematically implement measures for this Act, including measures for substances subject to enforcement in 2026 and after.
- *4Act on the Regulation of Manufacture and Evaluation of Chemical Substances in Japan
- *5Safety Data Sheet: Documentation listing the names, respective hazards and toxicities, etc., of substances contained in chemical products in order to ensure their safe handling
(2) GHS Compliance and Provision of SDS for All Products
①Provision of SDS for All Products
JSR group has voluntarily adopted a policy of providing customers with environmental and safety information by preparing SDS not only for products subject to legal obligations and products containing hazardous substances, but for all products which contain polymers. All SDS prepared by JSR group are in compliance with JIS Z 7253, the Industrial Safety and Health Act in Japan, the Law concerning Pollutant Release and Transfer Register in Japan, and the Poisonous and Deleterious Substances Control Act in Japan.
Furthermore, in order to provide customers with SDS that contain the most accurate information possible, we were early adopters of an SDS electronic data management system, which we have operated since its creation in 2002. This system includes user management, chemical substance database management, creation support, and publication (revision) history, and it allows us to accurately and quickly provide environmental and safety information related to JSR group products.
②GHS Compliance
GHS*6 is an international standard for (ⅰ) classification of chemical products according to hazard and toxicity; (ⅱ) labeling on product packaging and containers; and (ⅲ) documentation and provision of details in the SDS.
In Japan, the Industrial Safety and Health Act and the Law concerning Pollutant Release and Transfer Register stipulate mandatory application of GHS on the labels and SDS of products containing GHS-designated chemical substances, with GHS classification stipulated with JIS Z 7252 and SDS and other communicated information stipulated with JIS Z 7253. At JSR group, we perform GHS-based hazard and toxicity classification and create appropriate labels, as well as provide SDS, for all of our domestic products that contain applicable substances. We will also promote the gradual switch to the GHS in line with the laws being enacted in each country for when we export products we have manufactured in Japan.
- *6Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labeling of Chemicals
(3) Education on Chemical Substance Regulations
JSR Corporation provides in-house training on chemical substance regulations in Japan and abroad every year.
In FY2024, we implemented training on new chemical substance control laws and regulations in Japan and abroad, the latest information on revisions to the Industrial Safety and Health Act, and global PFAS regulatory trends.
In addition, we launched an in-house portal site for chemicals in FY2021, and with that, we have established an environment where it is possible to refer to the latest information on laws/regulations and training materials up to the previous fiscal year when needed from the Intranet environment.
4. Response to Overseas Regulations Concerning Exported Chemicals, etc.
Countries around the world strengthened their chemical products laws and regulations in advance of 2020 as this was the target year for the WSSD 2020 Goal*7. This global trend to strengthen regulations will continue beyond 2021.
Following the EU’s enactment of the REACH Regulation in 2007, JSR group has confirmed regulatory trends such as substance registration each time they have been strengthened in countries. We respond to these without omission based on the business areas and structure of local subsidiaries. We describe our response to laws and ordinances in the major manufacturing and importing countries of JSR group below. In addition to these, we appropriately comply with chemical products laws and ordinances in many other countries including ASEAN nations.
- *7WSSD 2020 Goal :long-term goal for chemical substances management that was adopted by the 2002 World Summit on Sustainable Development. Currently, the Global Framework on Chemicals (GFC), adopted in 2023, is the new international framework for chemical substance management.
(1) EU (REACH Regulation compliance)
The REACH*8 Regulation is an EU law relating to the registration, evaluation, authorization and restriction of chemical products. It was enacted in June 2007. Under REACH, all chemical products whose total production or import volume within the EU is one ton or more must register safety testing results and other data for the chemical substances contained in them, regardless of whether they are new or existing substances, every year.
In order to ensure there is no disruption to our manufacture and import of products in Europe, we regularly check whether or not the substances JSR group utilizes require registration. In addition, we have also prepared for risks with respect to usage restrictions which may arise from future substance evaluations. Accordingly, we are sharing information with development departments and taking other steps to anticipate risk once evaluations commence.
- *8Registration, Evaluation, Authorization and Restriction of Chemicals
(2) United States
In the United States, new chemical substance reporting is overseen by the Environmental Protection Agency under the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA) and other related federal laws and regulations. JSR follows all the required legal procedures with regard to the manufacture and importation within the United States of substances not included on the list of existing chemical substances. Moreover, we work in conjunction with our local subsidiaries to flexibly respond to the new legal requirements in relation to the amended TSCA enforced in 2016. In addition, we ascertain regulatory trends accompanying the start of risk assessment and respond to them.
(3) China
Since the enactment of the Measures for Environmental Management of New Chemical Substances to govern the reporting of new chemical substances in China, JSR group follows the required legal procedures if exporting to China a substance not included in the “Inventory of Existing Chemical Substances in China.” The amended Measures for Environmental Management of New Chemical Substances went into effect from January 2021. We are working to ensure we will not make any omissions in registering new chemical substances based on this amended law in the future.
(4) Korea
In Korea, reporting of new chemical substances is governed by the Act on Registration and Evaluation of Chemical Substances (REACH)*9 and the Occupational Safety and Health Act (OSHA)*10. JSR group follows the procedures based on these laws in advance when manufacturing and importing within Korea substances not included on the list of existing chemical substances.
In addition, pre-reporting in the preliminary stage for the registration of existing chemical substances in accordance with the 2019 revisions to the Korean REACH Act has been completed through coordination between our business departments and local subsidiaries. We will advance measures to systematically register substances according to the amount of them we manufacture and import, which is being phased in from now on.
- *9Act on Registration and Evaluation of Chemical Substances
- *10Occupational Safety and Health Act
(5) Taiwan
In Taiwan, a registration system for new chemical substances was introduced based on the Toxic Chemical Substances Control Act*11 enacted in 2014. JSR follows the required legal procedures established in line with this system, including registration of existing chemical substances. Also, Taiwan instituted “Existing Chemical Substance Nomination,” with 106 target substances designated for registration in 2019. The registration deadline was the end of 2024, and JSR has completed its compliance in a structure according to each business with our Taiwan subsidiary playing a central role in this.
- *11 (old) “Toxic Chemical Substances Control Act.” Amended in January 2019 to expand the scope of controlled chemical substances; the name was also changed to “Toxic and Concerned Chemical Substances Control Act” in order to reflect this expansion.
5. Chemical Management within Supply Chain Management
JSR group incorporates processes for chemical management in CSR procurement, green procurement and other areas of the implementation flow as part of our supply chain management. In particular, from the standpoint of toxic chemicals management, we have introduced chemSHERPA as part of our green procurement, as it is the industry standard format for communicating toxic substances information, and this has helped ensure that we are able to smoothly and reliably relay information to suppliers and in-house handling departments, as well as to customers. Please refer to the following links for more information.
6. Industrial and International Measures
JSR Corporation is a member of the Japan Chemical Industry Association (JCIA). In addition to participating in the association’s working groups, we contribute by providing a part of research funding to the activities of the Long-range Research Initiative (LRI)*12 which is being promoted by the association as voluntary effort of the chemical industry.
- *12LRI (Long-range Research Initiative):
This is a long-term, international initiative supporting research into chemical substances that have an impact on the environment, and human health. It was begun as a voluntary global research grant initiative of the International Council of Chemical Associations (ICCA), and it is currently being advanced through the cooperative efforts of the chemical industries associations of Japan, the United States, and the EU. In Japan, the Japan Chemical Industry Association is advancing research with the following three objectives.- (1)Expansion of scientific knowledge of chemical substances and health and the environment
- (2)Promotion of the improvement of safety management capabilities for chemical substances through the advancement of new testing methods and screening tools
- (3)Support for public policy decisions based on scientific evidence

